Explain the Large Difference in Ka 2 Values
Up to 24 cash back 2-K a 13 x 10 5 b. The nature of the element electronegativity resonance and hybridization contribute to the acid strength.
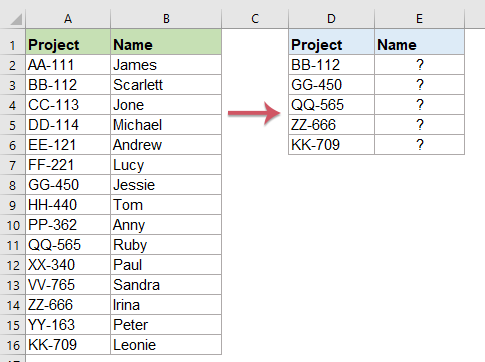
How To Compare Two Columns And Return Values From The Third Column In Excel
Larger the electron releasing tendency larger is the electron density on the carboxylic group and more basic is the compound.

. 10 10 9. In water strong and weak bases both establish an equilibrium value. This means that the acid has been dissociated partially.
Lets go a little further. ClO 4 -Perchlorate ion. Acids with a pK a value of less than about -2 are said to be strong acids.
So the first factor the atom does not explain this big difference in the acidity. We can use these equations to determine or of a weak base given of the conjugate acid. This equation makes it clear that the more the acid converts from its original form to its ionzied dissociated form the higher the Ka value.
Up to 10 cash back The higher the Ka the more the acid dissociates. Often times the K a value is expressed by using the pK a which is equal to latex-log_10K_alatex. How might you explain the difference between the pH values of the 001 M HCl pH 11 and the 001 M HC2H3O2 pH 36.
A mixture containing 0100 M HC 3 H 5 O 2 and 0100 M NaC 3 H 5 O 2 c. Strong acids are listed at the top left hand corner of the table and have Ka values 1 2. So pKa is the -log of Ka.
We can also use the value of at to derive other handy equations. Lets take our equation here Ka times Kb is equal to Kw. A large Ka favors the production_____.
Explain the large difference in the percent dissociation of the acid. The Ka value for most weak acids ranges from 10-2 to 10-14. Up to 24 cash back The reaction and the definition can then be written more simply.
For this reason K a values are generally reported for weak acids only. But if the value of A H is higher than HA then the Ka would be high and pKa would be low correspondingly. H_3O 10-25 000316 x Plug this value into the Ka equation to solve for Ka.
The larger the value of pKa the smaller the extent of dissociation. Compare the percent dissociation of the acid in a with the acid in d. A stronger acid will have a greater H concentration and hence a greater Ka.
The K D value relates to the concentration of antibody the amount of antibody needed for a particular experiment and so the lower the K D value lower concentration and thus the higher the affinity of the antibody. K D and affinity are inversely related. For example if the MCB is rated at 10kA it means.
KA rating is known as the short circuit withstand capacity or ultimate breaking capacity of a circuit breaker. A weak acid has a pKa value in the approximate range of -2 to 12 in water. If the pH of a solution of a weak acid and the p K a are known the ratio of the concentration of the conjugate base to the concentration of the acid may be calculated.
Acids with a pK a less than around -2 are strong acids. If K a is small pK a is large little dissociation has occurred so the acid is weak. Calculate the pH of a solution which is 100 M HF and 100 M KF.
A small Ka value means little of the acid dissociates so you have a weak acid. Two neighboring economies have the above production function but they have different parameter values. In contrast a weak acid is less likely to ionize and release a hydrogen ion thus resulting in a less acidic solution.
The multiple parts are supposed to guide you through it but I still dont understand how do it. In order for the value of Ka to be low A H value should be lower than the value of HA. This relationship is very useful for relating and for a conjugate acid-base pair.
The principal equilibrium in a solution of NaHCO3 is HCO3- HCO3- H2CO3 CO32- Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant for this reaction. The larger the value of pK a the smaller the extent of dissociation. We can also calculate the or of a weak acid.
When the Ka value is very large the are _____ favored over the _____. The acidity and pKa values depend on the stability of a conjugate base. That would be the log of Ka times Kb is equal to the log of Kw.
It is an oxygen. The smaller the value of Ka the larger the value of p Ka the weaker the acid. Hence if the Cobb-Douglas production function puts 23 of the weight on capital and only 13 on labor then we can explain a 16-fold difference in.
Kb or the base dissociation constant is the equilibrium expression for bases. The logarithmic constant pKa is equal to -log10Ka. By their ionization constants.
Strong acids have large Ka values because they completely dissociate in water and weak acids have small Ka values. For this part I got that Keq Ka2 Ka1 and after looking up the values I got that. The Ka of an acid shows the strength or weakness of an acid.
A large Ka value indicates a strong acid because it means the acid is largely dissociated into its ions. How else might you explain the large difference in income between Richland and Poorland. Molar concentration sensitivity 10 -4 to 10 -6.
Ka is the only true measurement. 32 10 9. A weak acid has a pK a value in the approximate range of -2 to 12 in water.
If we take the negative of both sides of the Eq. Acids with a pKa value of less than about -2 are said to be strong acids. Hence Ka being lower pKa is higher using.
KA rating of an MCB or an MCCB is the maximum current it can safely interrupt in case of a short circuit. Any time you see a p in terms of acid-base chemistry it automatically signifies -log whatever is after p. I need help solving this problem.
If the current goes beyond this value the circuit breaker could be damaged. A larger Ka means a smaller pKa. Thus strong acids must dissociate more in water.
If 41 16 then it must be the case that 2 1 which in turn requires that alpha equals 23. Atlantis has a saving rate of 28 percent and a population growth rate of 1 percent per year. The log of Ka times Kb is the same thing as the log of Ka plus the log of Kb equal to the log of.
Answer 1 of 2. K a for HF 72 x 10-4. As a result Ka is lower for ethanoic acid since Ka is the dissociation constant of acids.
Acids with a pK a in the range of -2 to 12 in water are weak acids. This is because a higher pKa value indicates that Ka is low. Lets take the log of both sides.
If you have already realized that it is a result of resonance. Strong acids have large ionization constants that approach infinity weak acids have small ionization constants that approach zero. Ka 000316 2 10 - 000316 0000009986 099684 1002E-5 2.
It measures the strength of an acid. A large Ka value also means the formation of products in the reaction is favored. This indicates that it is a strong acid.
Acid with values less than one are considered weak. If K a is large pK a is small this means the acid is mostly dissociated so the acid is strong. Use your answer to part a to solve for the steady-state value of y as a function of s n g and δ.
Thats our answer 27 times 10 to the negative 11 is the Ka value for the methylammonium ion.
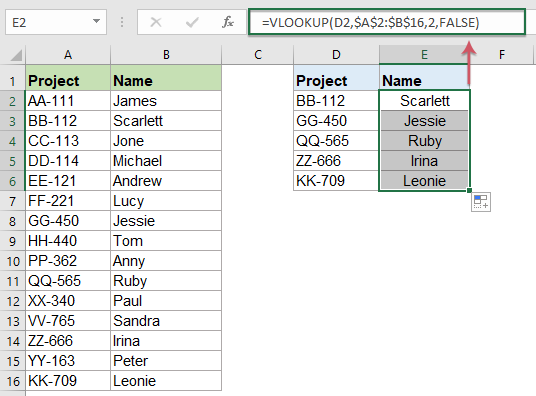
How To Compare Two Columns And Return Values From The Third Column In Excel

Pin By Shilpi Agrawal On School Number System Math Number System Number System Worksheets

How To Compare Two Columns And Return Values From The Third Column In Excel
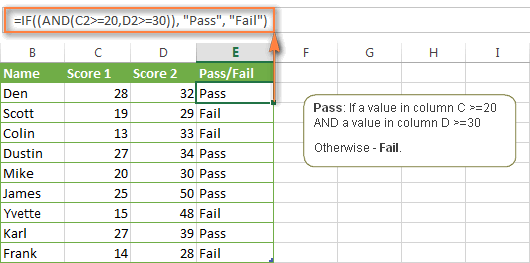
Excel If Statement With Multiple And Or Conditions Nested If Formulas Etc Ablebits Com
Comments
Post a Comment